FutureTask
# 基础
FutureTask 为 Future 提供了基础实现,如获取任务执行结果(get)和取消任务(cancel)等。如果任务尚未完成,获取任务执行结果时将会阻塞。一旦执行结束,任务就不能被重启或取消(除非使用runAndReset执行计算)。
FutureTask 常用来封装 Callable 和 Runnable,也可以作为一个任务提交到线程池中执行 。除了作为一个独立的类之外,此类也提供了一些功能性函数供我们创建自定义 task 类使用。
FutureTask 的线程安全由CAS来保证 。
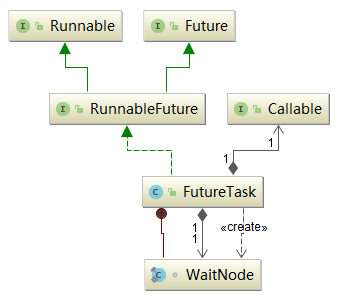
- 可以看到,FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,则RunnableFuture接口继承了Runnable接口和Future接口, 所以FutureTask既能当做一个Runnable直接被Thread执行,也能作为Future用来得到Callable的计算结果 。
# 源码深入
# Future接口
- Future接口代表异步计算的结果,通过Future接口提供的方法可以查看异步计算是否执行完成,或者等待执行结果并获取执行结果,同时还可以取消执行。Future接口的定义如下:
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
cancel(): cancel()方法用来取消异步任务的执行。如果异步任务已经完成或者已经被取消,或者由于某些原因不能取消,则会返回false。如果任务还没有被执行,则会返回true并且异步任务不会被执行。如果任务已经开始执行了但是还没有执行完成,若mayInterruptIfRunning为true,则会立即中断执行任务的线程并返回true,若mayInterruptIfRunning为false,则会返回true且不会中断任务执行线程。
isCanceled(): 判断任务是否被取消,如果任务在结束(正常执行结束或者执行异常结束)前被取消则返回true,否则返回false。
isDone(): 判断任务是否已经完成,如果完成则返回true,否则返回false。需要注意的是:任务执行过程中发生异常、任务被取消也属于任务已完成,也会返回true。
get(): 获取任务执行结果,如果任务还没完成则会阻塞等待直到任务执行完成。如果任务被取消则会抛出CancellationException异常,如果任务执行过程发生异常则会抛出ExecutionException异常,如果阻塞等待过程中被中断则会抛出InterruptedException异常。
get(long timeout,Timeunit unit): 带超时时间的get()版本,如果阻塞等待过程中超时则会抛出TimeoutException异常。
# 核心属性
//内部持有的callable任务,运行完毕后置空
private Callable<V> callable;
//从get()中返回的结果或抛出的异常
private Object outcome; // non-volatile, protected by state reads/writes
//运行callable的线程
private volatile Thread runner;
//使用Treiber栈保存等待线程
private volatile WaitNode waiters;
//任务状态
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0;
private static final int COMPLETING = 1;
private static final int NORMAL = 2;
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3;
private static final int CANCELLED = 4;
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5;
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6;
其中需要注意的是state是volatile类型的,也就是说只要有任何一个线程修改了这个变量,那么其他所有的线程都会知道最新的值。
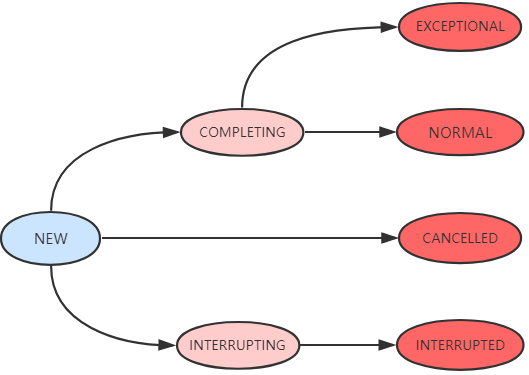
7种状态具体表示:
NEW: 表示是个新的任务或者还没被执行完的任务。这是初始状态。
COMPLETING: 任务已经执行完成或者执行任务的时候发生异常,但是 任务执行结果或者异常原因还没有保存到outcome字段 (outcome字段用来保存任务执行结果,如果发生异常,则用来保存异常原因)的时候,状态会从NEW变更到COMPLETING。但是这个状态会时间会比较短,属于中间状态。
NORMAL: 任务已经执行完成并且任务执行结果已经保存到outcome字段,状态会从COMPLETING转换到NORMAL。这是一个最终态。
EXCEPTIONAL: 任务执行发生异常并且异常原因已经保存到outcome字段中后,状态会从COMPLETING转换到EXCEPTIONAL。这是一个最终态。
CANCELLED: 任务还没开始执行或者已经开始执行但是还没有执行完成的时候,用户调用了cancel(false)方法取消任务且不中断任务执行线程,这个时候状态会从NEW转化为CANCELLED状态。这是一个最终态。
INTERRUPTING: 任务还没开始执行或者已经执行但是还没有执行完成的时候,用户调用了cancel(true)方法取消任务并且要中断任务执行线程但是还没有中断任务执行线程之前,状态会从NEW转化为INTERRUPTING。这是一个中间状态。
INTERRUPTED: 调用interrupt()中断任务执行线程之后状态会从INTERRUPTING转换到INTERRUPTED。这是一个最终态。 有一点需要注意的是,所有值大于COMPLETING的状态都表示任务已经执行完成(任务正常执行完成,任务执行异常或者任务被取消)。
各个状态之间的可能转换关系如下图所示:
# 构造方法
FutureTask(Callable<V> callable)
- 这个构造函数会把传入的Callable变量保存在this.callable字段中,该字段定义为private Callable<V> callable;用来保存底层的调用,在被执行完成以后会指向null,接着会初始化state字段为NEW。
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result)
这个构造函数会 把传入的Runnable封装成一个Callable对象保存在callable字段中 ,同时如果任务执行成功的话就会返回传入的result。这种情况下如果不需要返回值的话可以传入一个null。
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW;// ensure visibility of callable
}
# 核心方法-run()
- 在new了一个FutureTask对象之后,接下来就是在另一个线程中执行这个Task,无论是通过直接new一个Thread还是通过线程池,执行的都是run()方法,接下来就看看run()方法的实现。
public void run() {
//新建任务,CAS替换runner为当前线程
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);//设置执行结果
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);//处理中断逻辑
}
}
- 运行任务,如果任务状态为NEW状态,则利用CAS修改为当前线程。执行完毕调用set(result)方法设置执行结果。set(result)源码如下:
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v; //设置输出结果
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();//执行完毕,唤醒等待线程
}
}
分析:首先利用cas修改state状态为COMPLETING,设置返回结果,然后使用 lazySet(UNSAFE.putOrderedInt)的方式设置state状态为NORMAL。
- 结果设置完毕后,调用finishCompletion()方法唤醒等待线程,源码如下:
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {//移除等待线程
for (;;) {//自旋遍历等待线程
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);//唤醒等待线程
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
//任务完成后调用函数,自定义扩展
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
# 核心方法-get()
- FutureTask 通过get()方法获取任务执行结果。如果任务处于未完成的状态(state <= COMPLETING),就调用awaitDone方法(后面单独讲解)等待任务完成。任务完成后,通过report方法获取执行结果或抛出执行期间的异常。report源码如下:
//获取执行结果
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
//返回执行结果或抛出异常
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
# 核心方法-awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
- awaitDone用于等待任务完成,或任务因为中断或超时而终止。返回任务的完成状态。
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {//自旋
if (Thread.interrupted()) {//获取并清除中断状态
removeWaiter(q);//移除等待WaitNode
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;//置空等待节点的线程
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
//CAS修改waiter
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);//超时,移除等待节点
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);//阻塞当前线程
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);//阻塞当前线程
}
}
- 如果线程被中断,首先清除中断状态,调用removeWaiter移除等待节点,然后抛出InterruptedException。removeWaiter源码如下:
private void removeWaiter(WaitNode node) {
if (node != null) {
node.thread = null;//首先置空线程
retry:
for (;;) { // restart on removeWaiter race
//依次遍历查找
for (WaitNode pred = null, q = waiters, s; q != null; q = s) {
s = q.next;
if (q.thread != null)
pred = q;
else if (pred != null) {
pred.next = s;
if (pred.thread == null) // check for race
continue retry;
}
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,q, s)) //cas替换
continue retry;
}
break;
}
}
}
# 核心方法-cancel()
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
//如果当前Future状态为NEW,根据参数修改Future状态为INTERRUPTING或CANCELLED
if (!(state == NEW &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW,
mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))
return false;
try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {//可以在运行时中断
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();// 中断线程
} finally { // final state
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED);
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion();//移除并唤醒所有等待线程
}
return true;
}
尝试取消任务。如果任务已经完成或已经被取消,此操作会失败。
如果当前Future状态为NEW,根据参数修改Future状态为INTERRUPTING或CANCELLED。
如果当前状态不为NEW,则根据参数mayInterruptIfRunning决定是否在任务运行中也可以中断。中断操作完成后,调用finishCompletion移除并唤醒所有等待线程。
# 示例
# Future + ExecutorService
public class FutureDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future future = executorService.submit(new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (true) {
Long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
if ((current - start) > 1000) {
return 1;
}
}
}
});
try {
Integer result = (Integer)future.get();
System.out.println(result);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
# FutureTask + ExecutorService
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task = new Task();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(task);
executor.submit(futureTask);
executor.shutdown();
# FutureTask + Thread
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CallDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/
* 第三种方式:FutureTask + Thread
*/
// 2. 新建FutureTask,需要一个实现了Callable接口的类的实例作为构造函数参数
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(new Task());
// 3. 新建Thread对象并启动
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);
thread.setName("Task thread");
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] is running");
// 4. 调用isDone()判断任务是否结束
if(!futureTask.isDone()) {
System.out.println("Task is not done");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int result = 0;
try {
// 5. 调用get()方法获取任务结果,如果任务没有执行完成则阻塞等待
result = futureTask.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("result is " + result);
}
// 1. 继承Callable接口,实现call()方法,泛型参数为要返回的类型
static class Task implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Thread [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] is running");
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 100;++i) {
result += i;
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
return result;
}
}
}
